Know Your Diamond
Your Guide to Verification, Education & Better Understanding of Diamonds.Know Your diamond
Your Guide to Verification, Education & Better Understanding of Diamonds.
Verify Your Diamond
Our Promise of True, Genuine & Authentic Diamonds.
You can now get your diamond report verified by the International Gemological Institute directly on their website. Simply enter your report number in the search field here and get the result. It’s that simple!
Verification Report by

Diamond Education: 4Cs
Understanding the Basics
We have put together a Diamond Buying Guide for all your Diamond Jewellery purchases. It includes information on the major components that impact the beauty & value of a Diamond. This includes the widely accepted 4Cs, which are considered as a reliable source of Diamond knowledge world over.
Carat
The weight or size of a diamond is measured in carats (ct.).
One carat weighs 1/5 of a gram and is divided into 100 points, so a diamond weighing 1.07 ct. is referred to as “one carat and seven points.”
For example,
0.75 carat = 75 points
1/2 carat = 50 points
1/4 carat = 25 points
With an accuracy of 1/100,000 carat, the IGI scales provide a highly precise diamond weight, down to the hundredth or thousandth of a carat.
It is important to note that diamonds of the same weight don’t necessarily have the same size appearance. Those cut too shallow or deep may look small for their weight, or suffer in brilliance. As a reference, IGI recommends the following vertical spreads for round brilliant diamonds.
 When diamonds are mined, large gems are discovered much less frequently than small ones, which make large diamonds much more valuable.
When diamonds are mined, large gems are discovered much less frequently than small ones, which make large diamonds much more valuable.
Diamond prices rise exponentially with carat weight. So, a 2-carat diamond of a given quality is always worth more than two 1-carat diamonds of the same quality.
Colour
Most diamonds of gem quality used in jewelry vary in shade from completely colorless down to a visible yellow or brown tint.
The rarest and most expensive are diamonds in the colorless range graded D,E and F on a scale that descends to Z. Diamonds with more color than Z, or in other shades such as orange, pink, blue, etc. are classified as “Fancy Colored Diamonds” and are graded on the IGI Colored Diamond Report.
To determine the correct color, all submitted diamonds are compared to an internationally accepted master set of stones, the colors of which range from D, or colorless (the most sought after) to Z, the most yellow/brown – aside from “fancy” yellow or brown.
 IGI assigns a color grade for diamonds in the D-Z range with the diamond face-down and viewed through the pavilion. This is because size, shape, cut quality and the presence of fluorescence can influence visible face-up color. In fact, lighting, mounting choice and even the clothes one wears have an impact on color, so IGI uses the most neutral environment possible to ensure accurate and consistent results.
IGI assigns a color grade for diamonds in the D-Z range with the diamond face-down and viewed through the pavilion. This is because size, shape, cut quality and the presence of fluorescence can influence visible face-up color. In fact, lighting, mounting choice and even the clothes one wears have an impact on color, so IGI uses the most neutral environment possible to ensure accurate and consistent results.
Clarity
Since diamonds form under extreme heat and pressure, internal and external characteristics are common. These characteristics help gemologists separate natural diamonds from synthetics and simulants, and identify individual stones.
There are two types of clarity characteristics: inclusions and blemishes. In order to grade the clarity of a diamond, it is necessary to observe the number and nature of external and internal characteristics of the stone, as well as their size and position. The difference is based on their locations: inclusions are enclosed within a diamond, while blemishes are external characteristics. IGI grading reports show plotted diagrams of clarity characteristics marked in red for internal and green for external features.

Cut
While nature determined the color and clarity of a natural diamond, man is responsible for the cut quality which brings it to life. The planning, proportions, cutting precision and details of finish determine how brilliant, dispersive and scintillating the diamond will be. If the cutting factors under man’s control are not optimized, the appearance of the diamond can be adversely affected.
Diamond faceting has changed over time, particularly as lighting has evolved. There are many shapes and cutting styles, each with different visual properties. The most popular diamond in the age of modern electric lighting is the Round Brilliant.
 When a ray of light touches the surface, part of it is reflected back. This is called external refraction. The rest of the ray penetrates the stone and moves through it. This is known as refraction. The part of the ray reflected back to the surface exits, broken into spectral colors in a prism-like effect. This is known as dispersion. All of these elements contribute to the appearance of a diamond.
When a ray of light touches the surface, part of it is reflected back. This is called external refraction. The rest of the ray penetrates the stone and moves through it. This is known as refraction. The part of the ray reflected back to the surface exits, broken into spectral colors in a prism-like effect. This is known as dispersion. All of these elements contribute to the appearance of a diamond.
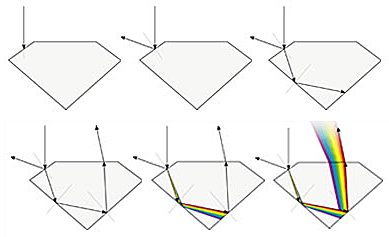 Elements of diamond beauty can be described as brilliance (all light returning to the eye), dispersion or ‘fire’ (seen as white light is broken into spectral colors), contrast patterns (contrasting light and dark areas created by the viewer’s reflection) and scintillation or ‘sparkle’ (seen as the diamond, the light source or the observer move). These qualities combine to create the life of the diamond and the way it reacts to lighting and environment.
Elements of diamond beauty can be described as brilliance (all light returning to the eye), dispersion or ‘fire’ (seen as white light is broken into spectral colors), contrast patterns (contrasting light and dark areas created by the viewer’s reflection) and scintillation or ‘sparkle’ (seen as the diamond, the light source or the observer move). These qualities combine to create the life of the diamond and the way it reacts to lighting and environment.
Jewellery Care Tips
Maintain & preserve Jewellery for a long time
Always
- Apply lotion, cosmetics, hairspray and perfume before dressing in jewelry.
- When undressing, wipe each piece with a clean soft cloth to remove oils and perspiration.
- Store in a fabric-lined box, separately or individually-wrapped in tissue to prevent scratches.
Never
- Never wear jewelry when doing physical work such as housekeeping, gardening or exercise.
- Never expose jewelry to household cleaning products.
- Never expose jewelry to chlorine swimming pools or hot tubs.
Cleaning Tips
- Follow the instructions appearing on the label or box.
- Clean in a secure location, not the rim of a sink where a piece may slip down the drain.
- Use only a soft brush, never sharp or hard objects, to remove dirt or particles.
- Clean your jewelry often; lotions, soaps and skin oils alter the optical properties of diamonds and gemstones, causing them to look dull.
- Seriously soiled jewelry should be cleaned professionally.
- Clean diamond jewelry with a soft brush dipped in warm water and mild detergent; rinse under running water.
- Never expose pearl jewelry to chemicals or solvents and store each piece in a soft bag.
- Don’t expose colored gemstones to chemicals, solvents or ultrasonics without knowing their specific cleaning requirements.
Longer Jewellery Life
- Keep your Laboratory Reports in a safe location, separate from jewelry pieces, for security.
- Have your jewelry cleaned and checked by a professional for worn mountings, loose prongs and general condition at least once per year.
- Have white gold re-plated, platinum re-polished and prongs re-tipped as necessary to maintain original condition (generally every 24 months or so).
- Have frequently-worn pearls restrung as necessary, with a knot between each pearl to prevent loss if the string breaks.
- Some colored gemstones should not be exposed to sudden temperature changes; know your pieces and their needs.
- Select daily-wear jewelry that is in harmony with your lifestyle and schedule of activities.
- Treat each piece as if it were a family heirloom, for someday it may be.
DAZZLE THE OCCASION.
MAKE HEADS TURN!
Looking to buy wedding jewellery, bridal jewellery, gold jewellery, diamond jewellery, platinum jewellery or silver jewellery in Bhavnagar, Gujarat? Visit Soni Dwarkadas Virchand Jewellers, and choose from a wide collection of exquisite masterpieces.